As rejuvenation biotechnology begins to take root, more and more biotech companies are joining the fight against aging. Here’s what’s happened in research, development, investment, and advocacy last month.
LEAF News
Our fifth annual conference, Ending Age-Related Diseases 2022, will be coming up next month. Our illustrious speakers will be delving deep into mechanisms of aging, organizational concerns, and many other topics related to longevity. Both paid and free tickets are available; register yours today!
Lifespan News
Saudi Government Begins Funding Longevity: A Saudi royal decree will provide the longevity industry with a billion dollars in funding via the Hevolution Foundation, a non-profit organization established by a Saudi Royal Decree and receiving funding from the Saudi government.
Vitamin D Supplements: A study published in GeroScience has uncovered a link between Vitamin D supplementation and a reduction of epigenetic age.
Vitamin B, Omega-3, and Cognitive Health: A new study details how Vitamin B and omega-3 fatty acids work together to improve brain health. Researchers publishing in the European Journal of Nutrition have discovered that a combination of B vitamins and the omega-3 fatty acid DHA is linked to decreased cognitive decline in older people.
Interviews
H+ DAO and Transhumanism with Dr. Natasha Vita-More: “Transhumanism is a philosophy, worldview, and a movement,” Dr. Natasha Vita-More states in the book “Transhumanism: What is it?” Essentially, it’s the idea of being able to move beyond being human, and finding solutions to living longer, healthier lives.
Rejuvenation Roundup Podcast
Ryan O’Shea of Future Grind hosts this month’s podcast, showcasing the events and research discussed here.
Journal Club
Species Somatic Mutation and Lifespan Correlation: This month’s Journal Club took a look at a recent paper published in Nature that explored species somatic mutation and lifespan correlation.
Research Roundup
Fighting Alzheimer’s Disease with Increased Autophagy: In a new study published in Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, researchers have shown that a combination of two compounds targeting different autophagy pathways is effective in fighting the pathological mechanism of Alzheimer’s disease in a mouse model.
 Senolytic Interventions Ameliorate Radiation Damage in Mice: In their publication in eLife Sciences, researchers at Newcastle University in the UK have illustrated how radiation-induced damage can be somewhat ameliorated with senolytics. These researchers focused on navitoclax along with the well-known combination of dasatinib and quercetin.
Senolytic Interventions Ameliorate Radiation Damage in Mice: In their publication in eLife Sciences, researchers at Newcastle University in the UK have illustrated how radiation-induced damage can be somewhat ameliorated with senolytics. These researchers focused on navitoclax along with the well-known combination of dasatinib and quercetin.
Antibody Therapy Alone Eliminates Certain Rectal Cancers: Researchers publishing in the New England Journal of Medicine have been able to completely eliminate stage 2 and 3 rectal tumors with a single monoclonal antibody drug. With the exception of skin cancer, colorectal cancer is the third most commonly diagnosed cancer in the US.
 Spermidine Human Trial Results Fail to Impress: The results of a human clinical trial for spermidine against cognitive decline have recently been published, but the results are not positive. Spermidine is a polyamine, meaning it has two or more primary amino groups. It is naturally occurring and is widely encountered in ribosomes and living tissues.
Spermidine Human Trial Results Fail to Impress: The results of a human clinical trial for spermidine against cognitive decline have recently been published, but the results are not positive. Spermidine is a polyamine, meaning it has two or more primary amino groups. It is naturally occurring and is widely encountered in ribosomes and living tissues.
Drug Leads to Drastic Weight Loss With Diet and Exercise: A large Phase 3 study published in the New England Journal of Medicine shows that an existing drug combined with a healthy diet and mild exercise leads to an average weight loss of 20%, mitigating an important reason why moderate exercise regimes do not always work.
 Urolithin A Improves Muscle Strength in Middle-Aged Adults: A new study published in Cell Reports Medicine shows that urolithin A supplementation improves muscle strength, fitness, and mitochondrial health in overweight, middle-aged adults. Some dose-specific molecular responses were reported in this study, which calls for further investigation.
Urolithin A Improves Muscle Strength in Middle-Aged Adults: A new study published in Cell Reports Medicine shows that urolithin A supplementation improves muscle strength, fitness, and mitochondrial health in overweight, middle-aged adults. Some dose-specific molecular responses were reported in this study, which calls for further investigation.
Vitamin D Supplements Linked to Slower Epigenetic Aging: Using a Berlin cohort, a study published in GeroScience has uncovered a link between Vitamin D supplementation and a reduction of epigenetic age. This study’s cohort consisted of 60- to 85-year-old participants in the Berlin Aging Study II (BASE-II).
 Mediterranean Diet Associated with Lifespan and Healthspan: Scientists have shown yet again that adherence to the Mediterranean diet is positively correlated with longer and healthier lives, this time in a large-scale population study spanning 130 countries.
Mediterranean Diet Associated with Lifespan and Healthspan: Scientists have shown yet again that adherence to the Mediterranean diet is positively correlated with longer and healthier lives, this time in a large-scale population study spanning 130 countries.
Scientists Discover Therapy Against Aggressive Breast Cancer: Publishing in Nature, scientists from the University of Texas report the discovery of a small molecule that can stop an especially aggressive subtype of breast cancer. Breast cancer remains the fourth deadliest type of cancer, claiming more than 40 thousand victims a year, almost exclusively women, in the US alone.
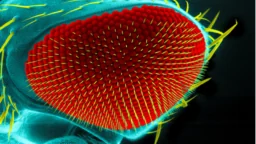 Dietary Restriction Delays Eye Aging in Flies: A new study published in Nature has reported on how caloric restriction, circadian rhythms, and molecular clocks interact to affect the ocular health and lifespan of fruit flies. The researchers begin their paper by discussing the concept of circadian rhythms, which are the 24-hour cycles that organisms have evolved for life on Earth.
Dietary Restriction Delays Eye Aging in Flies: A new study published in Nature has reported on how caloric restriction, circadian rhythms, and molecular clocks interact to affect the ocular health and lifespan of fruit flies. The researchers begin their paper by discussing the concept of circadian rhythms, which are the 24-hour cycles that organisms have evolved for life on Earth.
Blood Donation Slows Skin Aging in Mice: Scientists have shown that blood donation strongly affects skin aging in mice, probably by lowering the levels of toxic free iron. The treatment also decreased the percentage of fat in the liver and the size of adipocytes; adipocyte hypertrophy is a sign of fat tissue dysfunction.
 Skin Aging of the Naked Mole Rat: Naked mole rats are long-lived rodents famous for their resistance to cancer and sustained healthy lifespan. In a new study published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, researchers have shown that the skin of older members of this species is characterized by high expression of longevity-associated and tumor-suppressing genes.
Skin Aging of the Naked Mole Rat: Naked mole rats are long-lived rodents famous for their resistance to cancer and sustained healthy lifespan. In a new study published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, researchers have shown that the skin of older members of this species is characterized by high expression of longevity-associated and tumor-suppressing genes.
Targeting Fibrosis Reverses Ovarian Aging in Mice: Scientists have successfully treated ovarian aging in mice with compounds that target fibrosis and promote mitochondrial health. Ovarian aging is fascinating because one bodily system completely shuts down while the rest of the body is still in good health.
 B Vitamins and Omega-3 Fatty Acids Against Cognitive Decline: Researchers publishing in the European Journal of Nutrition have discovered that a combination of B vitamins and the omega-3 fatty acid DHA is linked to decreased cognitive decline in older individuals.
B Vitamins and Omega-3 Fatty Acids Against Cognitive Decline: Researchers publishing in the European Journal of Nutrition have discovered that a combination of B vitamins and the omega-3 fatty acid DHA is linked to decreased cognitive decline in older individuals.
Aspirin Affects Alzheimer’s Outcomes in Cardiac Patients: A study published in Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy has shown that low-dose aspirin affects Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia only in the presence of coronary heart disease. Aspirin is often taken at a steady, low dose of 100 to 300 milligrams a day in order to stave off cardiovascular diseases.
 Stem Cells for Fighting Sarcopenia: In their publication in Stem Cell Research & Therapy, a team of researchers has shown how effective mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) are in a mouse model. As multipotent stem cells, MSCs can differentiate into several different cell types, including fat cells, neurons, and bone cells.
Stem Cells for Fighting Sarcopenia: In their publication in Stem Cell Research & Therapy, a team of researchers has shown how effective mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) are in a mouse model. As multipotent stem cells, MSCs can differentiate into several different cell types, including fat cells, neurons, and bone cells.
Senolytic Helps Anti-Osteoarthritis Potential in Stem Cells: Scientists have improved the potential effectiveness of a stem cell therapy for osteoarthritis by targeting senescent cells. Osteoarthritis is an age-related disease that affects joints by degrading cartilage. While not fatal in itself, osteoarthritis negatively affects mobility and quality of life, and it can decrease lifespan and healthspan.
 The Relationship Between Diet and Senescence: An extremely comprehensive review published in Food Science & Biotechnology has summarized the current state of research regarding cellular senescence and basic dietary components.
The Relationship Between Diet and Senescence: An extremely comprehensive review published in Food Science & Biotechnology has summarized the current state of research regarding cellular senescence and basic dietary components.
Cocoa Extract Reduces Cardiovascular Mortality: A large-scale, randomized, controlled trial has found that in aging adults, cocoa extract does not affect the prevalence of adverse cardiovascular events but decreases their lethality.
 Longevity Through Altering Essential Gene Expression: In a new study published in GeroScience, researchers have shown that it is possible to significantly increase yeast lifespan by overexpressing genes highly conserved across various species.
Longevity Through Altering Essential Gene Expression: In a new study published in GeroScience, researchers have shown that it is possible to significantly increase yeast lifespan by overexpressing genes highly conserved across various species.
Metformin Is Linked to Weaker Exercise Improvements: A study published in Obesity has shown that metformin may decrease the gains in cardiorespiratory performance brought on by exercise.
Modifiying Retrons for Better Gene Editing: A new study published in Nature Chemical Biology has described an advancement in the use of retrons, a novel method of genetic engineering that may become superior to CRISPR technology.Omega‐3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Intake and Blood Pressure: A Dose‐Response Meta‐Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials: Doses of omega‐3 fatty acid intake above the recommended 3 grams per day may be associated with additional benefits in lowering blood pressure among groups at high risk for cardiovascular diseases.
Long-term Outcomes of Adding Lutein/Zeaxanthin and ω-3 Fatty Acids to the AREDS Supplements on Age-Related Macular Degeneration Progression: Beta carotene usage nearly doubled the risk of lung cancer, whereas there was no statistically significant increased risk with lutein/zeaxanthin.
Association between Dietary Inflammatory Index and serum Klotho concentration among adults in the United States: There was a dose–response relationship between DII and serum Klotho concentrations, suggesting that adhering to an anti-inflammatory diet has beneficial effects on aging and health by increasing the serum Klotho concentration.
Exercise increases the release of NAMPT in extracellular vesicles and alters NAD+ activity in recipient cells: The release of small EVs into the bloodstream is stimulated following moderate-intensity exercise in humans.
An exercise-inducible metabolite that suppresses feeding and obesity: These data define a conserved exercise-inducible metabolite that controls food intake and influences systemic energy balance.
Identification of healthspan-promoting genes in Caenorhabditis elegans based on a human GWAS study: The researchers name three specific genes that may be partially responsible for longevity.
Molecular mechanisms of exceptional lifespan increase of Drosophila melanogaster with different genotypes after combinations of pro-longevity interventions: The transcriptome analysis showed an impact of epigenetic alterations, lipid metabolism, cellular respiration, nutrient sensing, immune response, and autophagy.
Epigenetic aging: Biological age prediction and informing a mechanistic theory of aging: The researchers believe that the focus must shift from chasing increasingly accurate age computations to understanding the links between the epigenome and the mechanisms and physiological changes of aging.
Senotherapy Protects Against Cisplatin-Induced Ovarian Injury by Removing Senescent Cells and Alleviating DNA Damage: Collectively, this work indicates that senotherapies might prevent cisplatin-induced ovarian injury by removing senescent cells and reducing DNA damage, which represent a promising therapeutic avenue to prevent chemotherapy-induced ovarian damage.
Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate aging-associated skeletal muscle atrophy and dysfunction: Mesenchymal stromal cells exert immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects and could yield beneficial effects in aging-related degenerative disease.
Metformin, Rapamycin, or Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Pretreatment Attenuate Cognitive Impairment After Cerebral Hypoperfusion: These compounds could protect or attenuate cognitive impairment and white matter lesions by modifying microglial polarization and inhibiting phagocytosis.
Diverse aging rates in ectothermic tetrapods provide insights for the evolution of aging and longevity: Controlling for phylogeny and body size, ectotherms display a higher diversity of aging rates compared with endotherms and include phylogenetically widespread evidence of negligible aging.
The comparative mortality of an elite group in the long run of history: an observational analysis of politicians from 11 countries: These results show large relative and absolute inequalities favouring politicians in every country.
Impact of Beer and Nonalcoholic Beer Consumption on the Gut Microbiota: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Trial: Drinking nonalcoholic or alcoholic beer daily for 4 weeks did not increase body weight and body fat mass and did not significantly change serum cardiometabolic biomarkers.
News Nuggets
 NMN Human Trial Results Published: The data from a multicenter NMN clinical trial have been published with some very modest but still interesting results. The goal of this study was to determine if NMN has any influence on aging in humans. NAD+ was chosen as its primary endpoint, and its increase was used as an indication of an anti-aging effect.
NMN Human Trial Results Published: The data from a multicenter NMN clinical trial have been published with some very modest but still interesting results. The goal of this study was to determine if NMN has any influence on aging in humans. NAD+ was chosen as its primary endpoint, and its increase was used as an indication of an anti-aging effect.
 Maximon Startup AVEA Closes 2.5M CHF Funding Round: The longevity company builder Maximon has concluded a financing round for AVEA at this year’s World Economic Forum. AVEA, the longevity supplement startup with the aim to improve healthspan, announced the closing of a 2.5 million CHF seed financing round led by Maximon.
Maximon Startup AVEA Closes 2.5M CHF Funding Round: The longevity company builder Maximon has concluded a financing round for AVEA at this year’s World Economic Forum. AVEA, the longevity supplement startup with the aim to improve healthspan, announced the closing of a 2.5 million CHF seed financing round led by Maximon.
NOVOS Reports Effectiveness Against DNA Damage: NOVOS, a company that develops science-based products to slow down aging, announced results of two studies demonstrating that the combination of ingredients in its products, NOVOS Core and NOVOS Boost, protects against DNA damage and cellular aging (senescence).
 Kickstarting DAO Funding with the Longevity Molecule Project: Founded with the aim of financing early-stage longevity research through innovative methods, VitaDAO funded its first opening project, The Longevity Molecule, just months after the DAO’s formation. The Longevity Molecule is led by Morten Scheibye Knudsen in cooperation with Copenhagen’s (Denmark) Scheibye-Knudsen Lab.
Kickstarting DAO Funding with the Longevity Molecule Project: Founded with the aim of financing early-stage longevity research through innovative methods, VitaDAO funded its first opening project, The Longevity Molecule, just months after the DAO’s formation. The Longevity Molecule is led by Morten Scheibye Knudsen in cooperation with Copenhagen’s (Denmark) Scheibye-Knudsen Lab.
Korolchuk Lab’s Early Research Gets $285,000 from VitaDAO: The laboratory of Viktor Korolchuk, Professor of Molecular Cell at Newcastle University, has received funding to research autophagy activators and ways in which they can help prevent age-related diseases. Defective autophagy inhibits the function of cells, such as DNA repair and metabolic processes, and it is linked to health issues, including cancer, diabetes, and immune disorders.
 VitaDAO Celebrates 1 Year of Funding Longevity Projects: June 2022 marked the first anniversary of VitaDAO passing its Gnosis Token Auction. Since its founding, the biotech DAO has invested over $2.5 million into more than 10 longevity projects with the aim of driving early-stage research in the field.
VitaDAO Celebrates 1 Year of Funding Longevity Projects: June 2022 marked the first anniversary of VitaDAO passing its Gnosis Token Auction. Since its founding, the biotech DAO has invested over $2.5 million into more than 10 longevity projects with the aim of driving early-stage research in the field.
Molecule Raises $12.7 Million in Seed Funding for Biotech: Molecule, a comprehensive funding and incubation ecosystem for early-stage biopharma research, has raised $12.7 million in seed funding. The round was led by Northpond Ventures.