May 16, 2024
Exercise may be able to remove senescent cells only if acute inflammation is allowed to occur, according to a new study published in Aging. Inflammation and senescence Inflammation is known to be a critical part of aging, and its chronic accumulation has been labeled as a hallmark of aging: inflammaging. The SASP, the cocktail of...
March 21, 2024
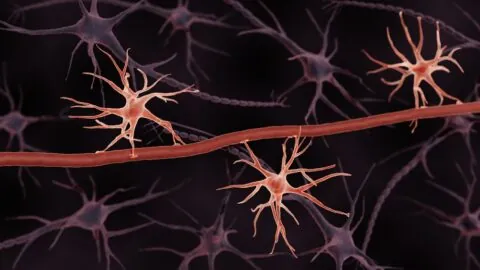
In an in-depth paper in Nature, researchers have explained how astrocytes, helper cells that provide crucial brain functions, epigenetically remember things in a way that encourages inflammation. Traumatized cells Long-lived immune cells, including T cells and B cells, can remember foreign pathogens [1]. This is why people can become immune to diseases after catching them...
February 22, 2024
A recent preprint paper from researchers at Sachi Bio has described how this company's technology can be used to alleviate brain inflammation in a mouse model. The problem of tau Along with the infamous amyloid beta, tau is well-known as a pathological factor in both Alzheimer's and regular aging [1]. The accumulation of tau with...
January 30, 2024
A new study suggests that the flavonoid epicatechin, found in chocolate, tea, and berries, provides robust protection against reperfusion injury in myocardial infarction [1]. Reperfusion injury: friendly fire Myocardial infarction (heart attack) is the injury caused by complete or partial cessation of blood flow to a portion of the myocardium, the heart’s muscle tissue. This,...
January 25, 2024
In a new paper in Cell Reports, researchers have named a little-known lipid as a core reason why inflammation decreases with fasting and may also shed light on how non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) work. Why high-calorie diets increase inflammation Previous research has identified the core reason why a high-calorie diet leads to inflammation. Excessive amounts...
November 14, 2023
A new study has identified a molecule found in Saposhnikovia root as a potent mediator of tendon regeneration in rats. The results were also replicated in human cells [1]. Aging does not spare tendons Like with many tissues, the health of tendons, which are central to mobility and agility, hinges on the function of local...