March 06, 2024
A recent Molecular Metabolism paper dives into the differences between intermittent and chronic rapamycin treatment and its differential impact on male and female mice [1]. The dark side of rapamycin Rapamycin doesn’t need much introduction in the lifespan extension community. This mTOR inhibitor has been shown multiple times to extend lifespan in animal studies. Because...
February 18, 2024
Reviewers have gone through the latest updates on studies featuring rapamycin and its derivatives in The Lancet Healthy Longevity. Testing a well-known longevity promoter Not many compounds actually extend life in healthy animals, but rapamycin is indeed one of them. These researchers report that its mechanism of action, the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR), is...
February 02, 2024
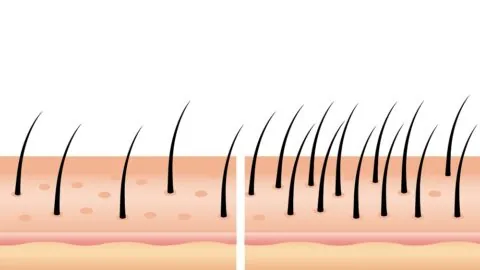
A new study has found that autophagy plays an important role in activating hair follicle stem cells and keeping the hair growth cycle going. By boosting autophagy, rapamycin improved hair growth in mice and in a human hair organ culture [1]. Round and round it goes The hair leads a cyclical life. First, a hair...
January 17, 2024
A review recently published in BMC Biology suggests that taking gerotherapeutics while exercising doesn’t have advantages over separate treatments [1]. Are two approaches better than one? Exercise is a well-established intervention that ameliorates several aspects of aging. Similarly, other research suggests that certain drugs, known as gerotherapeutics, target biological processes in a way that benefits...
January 09, 2024
A new review authored by three acclaimed geroscientists paints a promising picture of past and ongoing human clinical trials of prospective anti-aging drugs [1]. From worms and mice to humans The biology of aging is an exciting new field, but most of its successes have been in animal models, from the early breakthroughs in yeast...
January 08, 2024
Researchers have described how specialized nanoparticles, which deliver rapamycin and the antioxidant astaxanthin, restore macrophage balance and reduce inflammation in a mouse model of osteoarthritis. A matter of polarization Inflammation is a critical part of arthritis. Previous studies have found that inflammation of the membranes in joints (synovitis) strongly contributes to osteoarthritis [1]; in fact,...