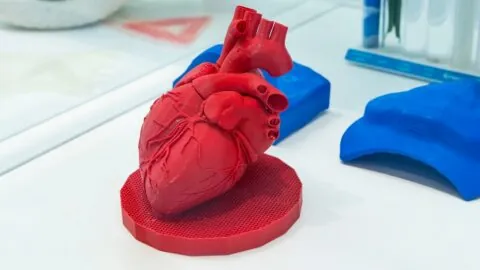
January 31, 2025
German scientists have created lab-grown “patches” of heart muscle tissue derived from pluripotent stem cells. Following a success with rhesus monkeys, they have obtained approval for a human trial [1]. Wear and tear As one of the most hard-working tissues in the body, the heart muscle is subject to incessant wear and tear due to...
January 30, 2025
Researchers have devised a method of reducing brain inflammation by creating a long-lasting inhibitor of the inflammatory factor NF-κB. Targeting inflammaging at its roots This study, published in the Nature journal Experimental & Molecular Medicine, begins with a discussion of age-related chronic inflammation (inflammaging) and its contributions to aging. Specifically, the researchers focus on neuroinflammation,...
January 29, 2025
On February 4-5, 2025, Hevolution Foundation will hold its second Global Healthspan Summit (GHS) in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. The two-day event at the Four Seasons Hotel brings together international attendees, including world leaders, policymakers, researchers & scientists, and experts from the biotechnology, pharmaceutical, healthcare, and private sectors, to explore innovative solutions in the rapidly advancing...
January 29, 2025
A new study suggests that low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) can be beneficial in eliminating senescent cells through the recruitment and activation of immune cells [1]. The double-edged sword of the SASP One of the characteristics of an aging organism is the accumulation of senescent cells. Various approaches are being developed to remove or neutralize those...
January 28, 2025
Scientists have presented GroceryDB, an open-access online database that measures the degree of processing of tens of thousands of products sold in three major US grocery chains [1]. What is ultra-processed food? While there is no universally accepted definition, the NOVA food classification system is widely used, and it defines ultra-processed food as “industrially manufactured...
January 27, 2025
In Cell Metabolism, researchers have described how a microRNA (miRNA) derived from exosomes generated by human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) restores function and fights senescence in cell cultures and mice. Looking for a better senomorphic Why We Age: Cellular SenescenceAs your body ages, more of your cells become senescent. Senescent cells do not divide or...