July 05, 2023
New research published in Scientific Reports suggests that microbes in the human gut and mouth can impact how long people live [1]. Bacteria and other microbes are often associated with diseases, but disease-causing microbes are only a minority. The majority of microbes are harmless or beneficial to humans, and we have millions of them living...
June 20, 2023
Scientists have found that the tumor microenvironment in lung adenocarcinoma favors methionine-producing bacteria, which, in turn, help the cancer survive nutrient scarcity [1]. Micro-friends or micro-foes? Our bodies host a mind-bending number of microorganisms, but most effects of this cohabitation are not well understood. Scientists have unearthed links between oral and gut microbiota and aging...
January 11, 2023
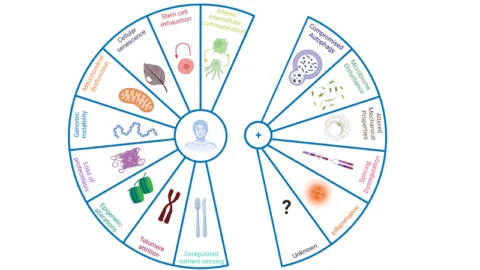
The year 2023 started with the publication of two remarkable review papers in Cell and Cell Metabolism by researchers addressing the hallmarks of aging and their interplay with the hallmarks of cancer [1,2]. These papers were authored by the same team that published the original 2013 Hallmarks of Aging paper [3]. The Reasons We Age...
October 19, 2022
In a new study published in Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, the researchers have shown that air pollution leads to lung function decline accompanied by lung and intestinal microbiome disbalances [1]. Air quality and longevity It is widely accepted that both intrinsic and extrinsic factors influence lifespan. Extrinsic factors include both lifestyle choices and environmental factors...
August 29, 2022
Publishing in Aging five months after their panel discussion in Copenhagen, many well-known researchers have explained their reasons for wishing to add new hallmarks of aging to the existing paradigm. A new addition to an old paradigm What is Aging? The Nine Reasons We AgeAging is a series of processes that include direct damage, accumulation...
September 24, 2021
A study conducted in Sweden and published in Scientific Reports has outlined the relationship between aging and the metabolites present in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which cushions and supports the brain and spine. A detailed, metabolic analysis The researchers extracted CSF from 41 people aged 20 to 74 who don't have neurological disorders. They investigated somewhat...